1. 摘要
在Java I/O体系中,File类是唯一代表磁盘文件本身的对象。
File类定义了一些与平台无关的方法来操作文件,包括检查一个文件是否存在、创建、删除、重命名、判断文件的读写权限、设置和查询文件的最近修改时间等操作。
值得注意的地方是,Java中通常的File并不代表一个真是存在的文件对象,当你通过指定的一个路径扫描时,它就会返回一个代表这个路径相关联的一个虚拟对象,这个对象可能是一个真是存在的文件或者是一个包含多个文件的目录。
2. File 类介绍
File类没有无参构造方法,最常用的是使用下面的构造方法来生成File对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
File file = new File(FILE_PATH);
System.out.println(file.getName());
File file1 = new File("/Users/xiaoyuge/Desktop", "1.txt");
System.out.println(file1.getName());
|
File类中定义类很对关于File 对象的一些操作方法,例如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
|
public class FileDemo {
public static final String FILE_PATH = "/Users/xiaoyuge/Desktop/txt/1.txt";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File(FILE_PATH);
if (file.exists()) {
System.out.println("文件存在");
} else {
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("文件不存在,创建一个文件");
}
File parentFile = file.getParentFile();
if (parentFile.exists()) {
System.out.println("文件目录存在");
} else {
parentFile.mkdirs();
System.out.println("文件目录不存在,创建");
}
if (parentFile.isDirectory()) {
System.out.println("父节点是一个目录");
}
File[] files = parentFile.listFiles();
for (File f : files) {
System.out.println(f + ";");
}
File file2 = files[0];
System.out.println("文件名:" + file2.getName());
System.out.println("路径:" + file2.getPath());
System.out.println("绝对路径:" + file2.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("父文件夹名:" + file2.getParent());
System.out.println(file2.exists() ? "存在" : "不存在");
System.out.println(file2.canWrite() ? "可写" : "不可写");
System.out.println(file2.canRead() ? "可读" : "不可读");
System.out.println(file2.canExecute() ? "可执行" : "不可执行");
System.out.println(file2.isDirectory() ? "目录" : "不是目录");
System.out.println(file2.isFile() ? "是文件" : "不是文件");
System.out.println(file2.isAbsolute() ? "是绝对路径" : "不是绝对路径");
System.out.println("最后一次修改时间:" + file2.lastModified());
System.out.println("文件大小:" + file2.length());
File newFile = new File(file2.getParentFile(),"2.txt");
file2.renameTo(newFile);
file2.delete();
file2.deleteOnExit();
}
}
|
需要注意的地方:
3. 文件的读写操作
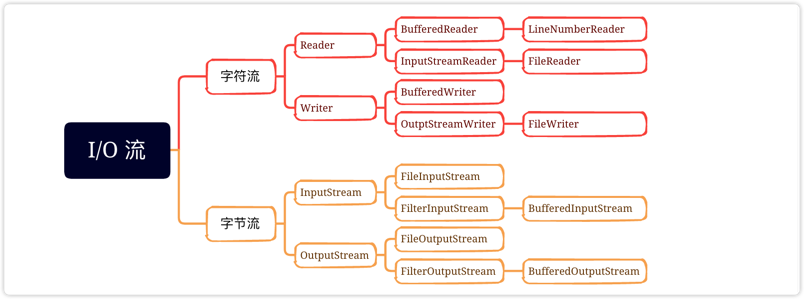
对文件的读写,可以通过字节流或者字符流接口来完成,不管那种方式,大致分为一下几个步骤:
获取文件file对象
通过file对象,获取一个字节流或者字符流接口对象,进行读写操作
关闭文件流
3.1 通过字节流写入
字节流接口的文件写入,可以通过OutputStream下的子类FileOutputStream来实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public class FileWriteDemo {
public static final String FILE_PATH = "/Users/xiaoyuge/Desktop/txt/22.txt";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File(FILE_PATH);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
String content = "通过字节流写入";
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
outputStream.write(content.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
outputStream.close();
}
}
|
上面的操作方式会覆盖原始的数据,如果想在已有的文件里面追加数据,可以使用下面的方式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
String content = "-----这是追加的部分-----";
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file, true);
outputStream.write(content.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
outputStream.close();
|
3.2 通过字节流读取
字节流读取文件,可以通过InputStream下的子类FileInputStream来实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| public class FileReadDemo {
public static final String FILE_PATH = "/Users/xiaoyuge/Desktop/txt/22.txt";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File(FILE_PATH);
if (file.exists()){
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = is.read(buffer)) > -1){
String msg = new String(buffer, 0, len, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println(msg);
}
is.close();
}
}
}
|
3.3 通过字符流写入
JDK 提供了Writer和Reader字符流接口,字符流写入可以通过Writer下的子类FileWriter来实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class FileWriteDemo {
public static final String FILE_PATH = "/Users/xiaoyuge/Desktop/txt/22.txt";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File(FILE_PATH);
if (!file.exists()){
file.createNewFile();
}
Writer writer = new FileWriter(file);
writer.write("hello xiaoyuge");
writer.write("\n");
writer.append("this is a demo");
writer.close();
}
}
|
3.4 通过字符流读取
字符流读取可以通过Reader下的子类FileReader来实现文件的数据读取
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| public class FileReadDemo {
public static final String FILE_PATH = "/Users/xiaoyuge/Desktop/txt/22.txt";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File(FILE_PATH);
if (file.exists()){
Reader reader = new FileReader(file);
char[] buffer = new char[1024];
int len;
while ((len = reader.read(buffer)) > -1){
String msg = new String(buffer, 0 , len);
System.out.println(msg);
}
reader.close();
}
}
}
|
3.5 文件拷贝
在实际的软件开发过程中,避免不了文件拷贝,通过以上的接口方法,可以很容易的写出一个文件复制的方法,以字节流操作为例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public static void main(String[]args){
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
InputStream input = new FileInputStream(new File("input.txt"));
OutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(new File("output.txt"));
int length;
while ((length = input.read(buffer)) != -1) {
output.write(buffer, 0, length);
}
input.close();
output.close();
}
|
除此之外,JDK也支持采用缓冲流读写技术来实现数据的高效读写
之所以高效,是因为字节缓冲流内部维护了一个缓冲区,读写是先将数据存入缓冲区中,当缓冲区满时,再将数据一次性读出/写入;这样可以减少与磁盘实际的I/O操作次数,可以显著提升读写效率
比如以字节流缓冲流为例,包装类分别是BufferedInputStream(字节流缓冲输入流) 和BufferedOutputStream(字节流缓冲输出流)
采用缓冲流拷贝文件,具体实现如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
InputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("/Users/xiaoyuge/Desktop/txt/input.txt"));
OutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("/Users/xiaoyuge/Desktop/txt/output.txt"));
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
bos.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
|
在大文件的拷贝中,使用缓冲流比不适用缓冲流技术至少快10倍。
4. 字节流和字符流互转
4.1 字节流转字符流
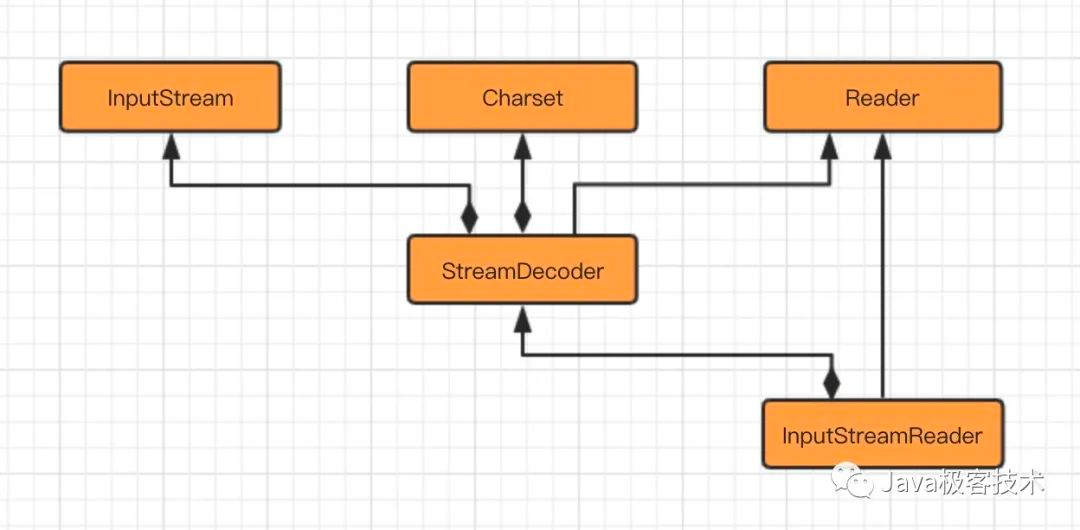
字节流转字符流的操作,主要体现在数据的读取阶段,转化过程如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File(FILE_PATH);
if (file.exists()){
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file);
Reader reader = new InputStreamReader(is,StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
char[] buffer = new char[1024];
int len;
while ((len = reader.read(buffer)) > -1) {
String msg = new String(buffer, 0, len);
System.out.println(msg);
}
reader.close();
is.close();
}
}
|
当读取数据的时候,先通过字节流读取,在转成字符流读取。
字节流转字符流需要指定编码规则,如果没有指定,会区当前系统的默认规则。
4.2 字符流转字节流
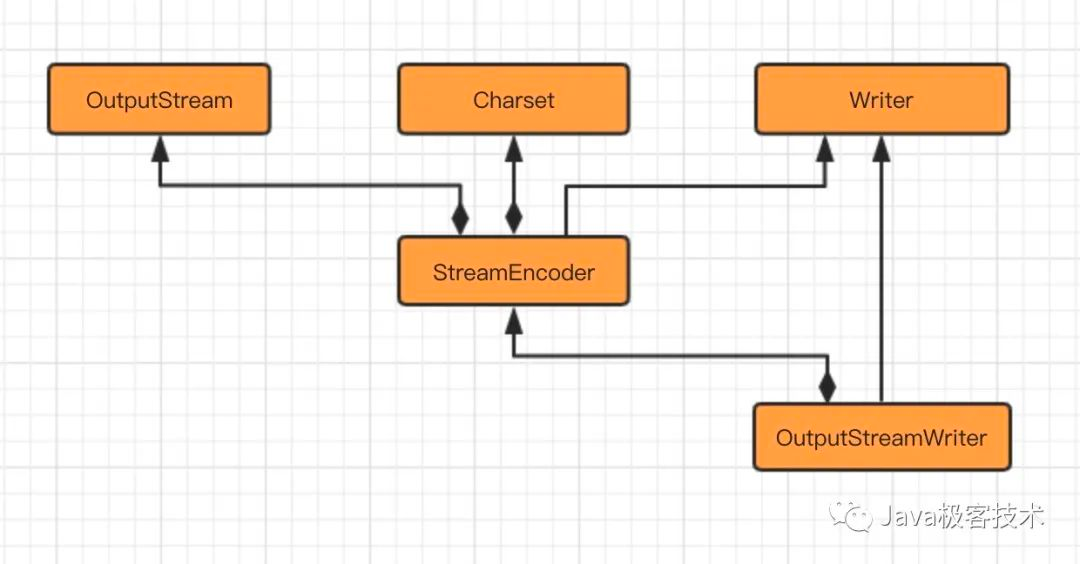
字符流转字节流的操作,主要体现在数据的写入阶段,转化过程如下图所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| public static void main(String[]args){
File file = new File("readWriteDemo.txt");
if(!file.exists()){
file.createNewFile();
}
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
Writer out = new OutputStreamWriter(outputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
out.write("Hello");
out.write("\n");
out.append("我们一起来学习Java");
out.close();
outputStream.close();
}
|
同样的,当写入数据的时候,先通过字符流写入,再转成字节流输出。
字符流转字节流,也需要指定编码规则,如果没有指定,会取当前系统默认的编码规则。





