1. 接口出现多个版本的原因 一般来说,RESTful API接口是提供给其他模块、系统或者公司使用的,不能随意频繁的变更。然后,需求和业务的不断变化,接口和参数也会发生相应的变化。
1.1 控制接口多版本的方式
同一实例 ,用注解隔离不同版本控制
api.baidu.com/v1/user 表示 v1版本的接口, 保持原有接口不动,匹配@ApiVersion(“1”)的handlerMapping
api.baidu.com/v2/user 表示 v2版本的接口, 更新新的接口,匹配@ApiVersion(“2”)的handlerMapping
2. 实现案例
这里主要演示的是第四种单一实例中控制接口的版本,基于Springboot封装了@ApiVersion注解方式控制好接口版本
2.1 自定义注解@ApiVersion 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Mapping public @interface ApiVersion { String value () ; }
2.2 定义版本匹配RequestCondition 版本匹配支持三层版本
v1.1.1(大版本,小版本,补丁版本)
v1.1 (等同于v1.1.0)
v1 (等同于v1.0.0)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 @Slf4j public class ApiVersionCondition implements RequestCondition <ApiVersionCondition > private static final Pattern VERSION_PREFIX_PATTERN_1 = Pattern.compile("/v\\d\\.\\d\\.\\d/" ); private static final Pattern VERSION_PREFIX_PATTERN_2 = Pattern.compile("/v\\d\\.\\d/" ); private static final Pattern VERSION_PREFIX_PATTERN_3 = Pattern.compile("/v\\d/" ); private static final List<Pattern> VERSION_LIST = Collections.unmodifiableList( Arrays.asList(VERSION_PREFIX_PATTERN_1, VERSION_PREFIX_PATTERN_2, VERSION_PREFIX_PATTERN_3) ); @Getter private final String apiVersion; public ApiVersionCondition (String apiVersion) this .apiVersion = apiVersion; } @Override public ApiVersionCondition combine (ApiVersionCondition other) return new ApiVersionCondition(other.apiVersion); } @Override public ApiVersionCondition getMatchingCondition (HttpServletRequest request) for (int vIndex = 0 ; vIndex < VERSION_LIST.size(); vIndex++) { Matcher m = VERSION_LIST.get(vIndex).matcher(request.getRequestURI()); if (m.find()) { String version = m.group(0 ).replace("/v" , "" ).replace("/" , "" ); if (vIndex == 1 ) { version = version + ".0" ; } else if (vIndex == 2 ) { version = version + ".0.0" ; } if (compareVersion(version, this .apiVersion) >= 0 ) { log.info("version={}, apiVersion={}" , version, this .apiVersion); return this ; } } } return null ; } @Override public int compareTo (ApiVersionCondition other, HttpServletRequest request) return compareVersion(other.getApiVersion(), this .apiVersion); } private int compareVersion (String version1, String version2) if (version1 == null || version2 == null ) { throw new RuntimeException("compareVersion error:illegal params." ); } String[] versionArray1 = version1.split("\\." ); String[] versionArray2 = version2.split("\\." ); int idx = 0 ; int minLength = Math.min(versionArray1.length, versionArray2.length); int diff = 0 ; while (idx < minLength && (diff = versionArray1[idx].length() - versionArray2[idx].length()) == 0 && (diff = versionArray1[idx].compareTo(versionArray2[idx])) == 0 ) { ++idx; } diff = (diff != 0 ) ? diff : versionArray1.length - versionArray2.length; return diff; } }
2.3 定义HandlerMapping 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class ApiVersionRequestMappingHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingHandlerMapping @Override protected RequestCondition<?> getCustomTypeCondition(@NonNull Class<?> handlerType) { ApiVersion apiVersion = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(handlerType, ApiVersion.class); return null == apiVersion ? super .getCustomTypeCondition(handlerType) : new ApiVersionCondition(apiVersion.value()); } @Override protected RequestCondition<?> getCustomMethodCondition(@NonNull Method method) { ApiVersion apiVersion = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, ApiVersion.class); return null == apiVersion ? super .getCustomMethodCondition(method) : new ApiVersionCondition(apiVersion.value()); } }
2.4 注册HandlerMapping 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Configuration public class CustomWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport @Override protected RequestMappingHandlerMapping createRequestMappingHandlerMapping () return new ApiVersionRequestMappingHandlerMapping(); } }
或者实现WebMvcRegistrations接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Configuration @RequiredArgsConstructor public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer , WebMvcRegistrations @Override @NonNull public RequestMappingHandlerMapping getRequestMappingHandlerMapping () return new ApiVersionRequestMappingHandlerMapping(); } }
2.5 测试运行 新建测试对象:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Data @Builder public class User private String name; private int age; }
测试方法:
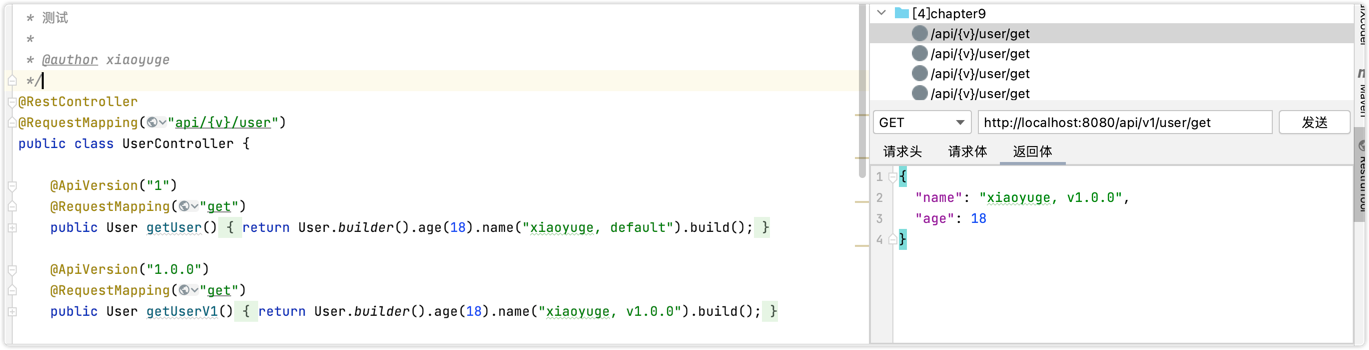
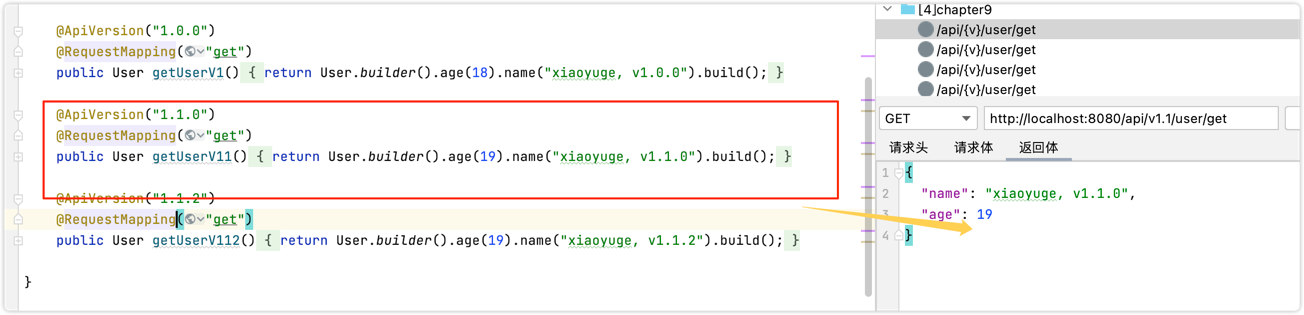
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 @RestController @RequestMapping("api/{v}/user") public class UserController @ApiVersion("1") @RequestMapping("get") public User getUser () return User.builder().age(18 ).name("xiaoyuge, default" ).build(); } @ApiVersion("1.0.0") @RequestMapping("get") public User getUserV1 () return User.builder().age(18 ).name("xiaoyuge, v1.0.0" ).build(); } @ApiVersion("1.1.0") @RequestMapping("get") public User getUserV11 () return User.builder().age(19 ).name("xiaoyuge, v1.1.0" ).build(); } @ApiVersion("1.1.2") @RequestMapping("get") public User getUserV112 () return User.builder().age(19 ).name("xiaoyuge, v1.1.2" ).build(); } }
测试结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 http://localhost:8080/api/v1/user/get // {"name":"xiaoyuge, v1.0.0","age":18} http://localhost:8080/api/v1.1/user/get // {"name":"xiaoyuge, v1.1.0","age":19} http://localhost:8080/api/v1.1.1/user/get // {"name":"xiaoyuge, v1.1.0","age":19} 匹配比1.1.1小的中最大的一个版本号 http://localhost:8080/api/v1.1.2/user/get // {"name":"xiaoyuge2, v1.1.2","age":19} http://localhost:8080/api/v1.2/user/get // {"name":"xiaoyuge2, v1.1.2","age":19} 匹配最大的版本号,v1.1.2
这样,如果我们向另外一个模块提供v1版本的接口,新的需求中只变动了一个接口方法,这时候我们只需要增加一个接口添加版本号v1.1即可用v1.1版本访问所有接口。
此外,这种方式可能会导致v3版本接口没有发布,但是是可以通过v3访问接口的;这种情况下可以添加一些限制版本的逻辑,比如最大版本,版本集合等。